How Fire Departments Use Simulation Training to Prepare for High-Risk Scenarios
November 13, 2024

Firefighting is one of the most crucial and dangerous professions in the world. Firefighters are often the first responders in emergencies, tackling life-threatening situations that require quick thinking and effective action. In recent years, simulation training has emerged as a fundamental method for preparing firefighting crews for high-risk scenarios. This article delves into how fire departments utilize simulation training, the types of simulations conducted, and the critical benefits derived from this innovative training approach.
1. The Importance of Simulation Training in Firefighting
Simulation training serves as an invaluable tool for fire departments as it provides realistic, hands-on experiences without the associated risks of real-life firefighting operations. The highly stressful nature of firefighting means that firefighters must be prepared to face various unpredictable situations, from structural fires to wildland blazes.
Fire departments recognize that traditional training exercises may not fully replicate the hazards faced on the job. Simulation training helps to bridge this gap by allowing firefighters to:
- Practice Decision-Making: Firefighting often requires rapid decision-making under extreme pressure. Simulations provide scenarios that help firefighters practice these quick-thinking skills in controlled environments.
- Enhance Physical Skills: Simulations allow firefighters to practice firefighting techniques, use equipment, and navigate complex environments safely and effectively.
- Build Team Cohesion: Many emergency situations require teamwork. Simulation training fosters communication and collaboration among team members, ensuring they function effectively under stress.
- Evaluate Performance: After simulations, departments can assess performance metrics, identifying areas of strength and opportunities for improvement.
Ultimately, simulation training aims to ensure that firefighters are as prepared as possible to tackle real-life emergencies while minimizing risks to themselves and the communities they serve.
2. Types of Simulation Training Exercises
Fire departments employ various types of simulation training exercises tailored to different scenarios and objectives. Here are some of the most common simulation types utilized in firefighting training:
2.1 Virtual Reality (VR) Simulations
Virtual reality technology offers immersive training experiences, allowing firefighters to navigate and practice firefighting techniques in simulated environments. These high-tech simulations can recreate environments like burning buildings or hazardous materials incidents.
Benefits of VR simulations include:
- Realistic visual and sensory immersion
- Opportunity to practice specific rescue techniques
- Safer environments for learning and practice
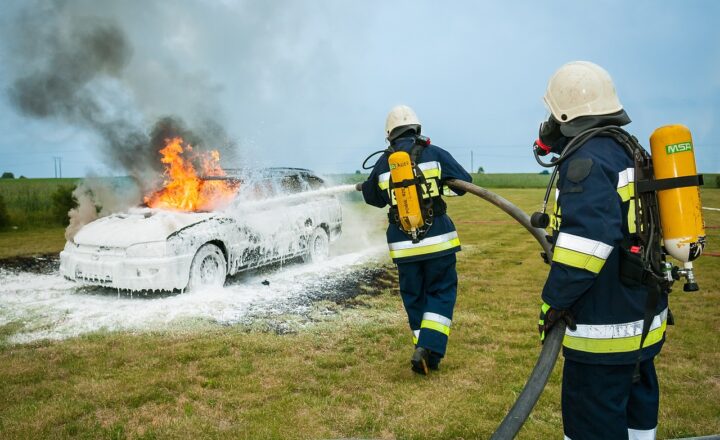
2.2 Live Fire Training Simulations
Live fire training exercises involve controlled burn scenarios where firefighters can practice extinguishing real fires with supervision. These exercises are typically held in training facilities designed specifically for fire training.
While live fire simulations present risks, they provide several advantages:
- Hands-on experience in handling real flames and heat
- Realistic assessments of initial response time and technique effectiveness
- Critical understanding of fire behavior and propagation
2.3 Mock Disaster Scenarios
In mock disaster simulations, firefighters practice responding to large-scale incidents, such as building collapses or mass casualty events. These scenarios integrate multiple teams and organizations (EMS, police, and local hospitals), emphasizing inter-agency coordination.
Key elements include:
- Testing communication and coordination skills across teams
- Real-time strategy management and resource allocation
- Assessment of incident command and leadership skills
2.4 Simulation Software Training
Simulation software can model various fire scenarios, allowing trainees to input conditions and create realistic simulation environments. This method supports strategic planning, allowing firefighters to visualize and strategize their approaches to different situations.
Benefits include:
- Ability to rehearse multiple strategies quickly
- Fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills
- Real-time feedback on decision-making outcomes
By providing options for diverse training environments, fire departments can prepare their crews effectively for any high-risk situation.
3. Benefits of Simulation Training in Firefighting
Simulation training offers numerous benefits for fire departments and their personnel. Some of the key advantages include:
3.1 Enhanced Skill Proficiency
Regular simulation training enables firefighters to refine their skills in a safe, controlled environment. With repeated practice, they become more competent and confident in performing life-saving techniques. This proficiency is crucial when every second counts in emergencies.
3.2 Improved Safety Awareness
By participating in simulations that replicate high-risk scenarios, firefighters learn to recognize hazards, assess risks, and respond appropriately. This heightened safety awareness is key to both their protection and the protection of civilians.
3.3 Reduced Response Times
Through practice and familiarization with various scenarios, firefighters can significantly reduce response times. With a well-trained crew, fire departments can better manage emergencies, maximizing efficiency and saving lives.
3.4 Increased Confidence and Morale
Simulation training fosters team spirit and unity among crew members. Feeling well-prepared and confident in their skills can lead to higher job satisfaction and morale, promoting a strong workplace culture within fire departments.
4. Challenges and Limitations of Simulation Training
While simulation training offers many advantages, some challenges must also be recognized:
4.1 High Costs
Investing in high-quality simulation technology and facilities can require a significant budget. For some departments, especially smaller volunteer-based units, these costs may be prohibitive.
4.2 Limited Realism
While simulations can closely mimic real-life situations, taking part in live operations is still essential to prepare firefighters fully. Simulations should complement, not replace, practical training.
4.3 Resistance to Change
Some fire department personnel may resist adopting new training methods. Overcoming this resistance requires effective communication and showcasing the proven benefits of simulation training.
5. The Future of Simulation Training in Fire Departments
As technology continues to evolve, so will simulation training in firefighting. Innovations like augmented reality (AR) and advanced artificial intelligence (AI) are expected to change how fire departments conduct training. These developments promise to enhance realism further and provide personalized training experiences for firefighters.
Ultimately, the role of simulation training in firefighting is set to grow, making it a staple in preparing crews for the challenges they will face. This investment not only improves firefighting performance but also ensures the safety of both firefighters and the communities they serve.
Conclusion
Simulation training has transformed how fire departments prepare their crews for high-risk scenarios. By providing realistic, hands-on experiences, firefighters develop the necessary skills, confidence, and teamwork essential for emergency response. As technology advances, simulation training will only become more sophisticated, further strengthening the firefighting profession and enhancing public safety.
Fire departments that prioritize effective simulation training will undoubtedly be better equipped to protect lives, manage emergencies efficiently, and foster a culture of safety and preparedness within their teams.