How Firefighters Are Trained to Handle Hazardous Materials and Dangerous Chemicals
November 14, 2024
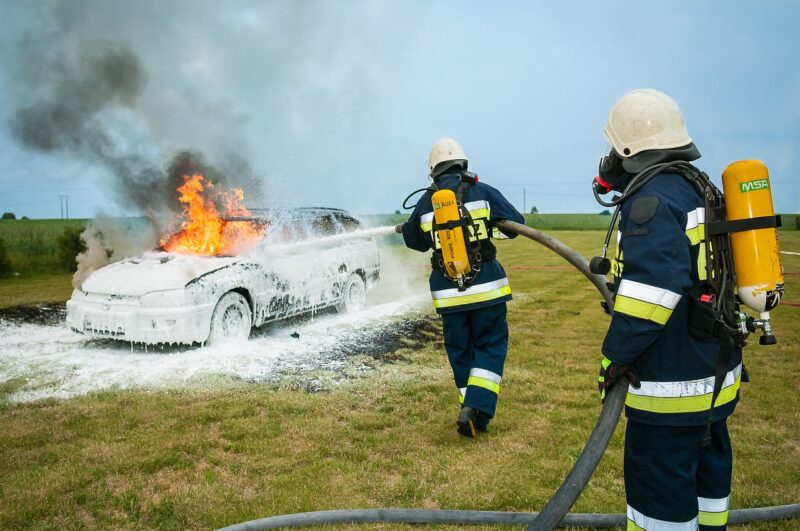

Firefighters are often seen as heroes, bravely confronting flames and saving lives. However, their responsibilities go far beyond battling blazes. One of the critical aspects of their training involves handling hazardous materials and dangerous chemicals. This article delves into the various components of firefighter training specific to hazardous materials, ensuring they are equipped to respond effectively in times of crisis.
1. The Importance of Hazardous Materials Training
In today’s society, the use of hazardous materials is prevalent in various sectors, including industry, transportation, and medical services. Firefighters need to be prepared for incidents involving:
- Chemical Spills: Accidents involving the release of harmful substances require immediate and knowledgeable response to minimize risks to public health and safety.
- Chemical Fires: Fires fueled by hazardous materials pose unique challenges, requiring specific firefighting strategies and techniques to contain and extinguish the flames safely.
- Terrorism and Environmental Hazards: The potential for terrorist attacks using hazardous materials or incidents resulting from natural disasters necessitates thorough training for firefighters to protect lives and mitigate damage.
Firefighter training in hazardous materials ensures that they can identify, assess, and manage emergencies involving dangerous substances effectively. Their expertise not only protects them but also the communities they serve.
2. Components of Hazardous Materials Training
Firefighters undergo rigorous training that focuses on various components aimed at preparing them for hazardous materials incidents:
a. Understanding Hazardous Materials
Firefighters learn about different types of hazardous materials, including:
- Flammable Liquids: Substances that can ignite easily, such as gasoline and solvents.
- Corrosive Materials: Chemicals that can destroy or permanently damage living tissue or severely corrode materials, like sulfuric acid.
- Toxic Substances: Materials harmful to human health if inhaled, ingested, or contacted, such as pesticides and industrial chemicals.
Understanding the properties of these materials allows firefighters to assess risks better and develop appropriate response plans.
b. Specialized Equipment Training
Firefighters are trained in the use of specialized equipment designed for hazardous materials incidents:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Firefighters are equipped with PPE that protects them from exposure to hazardous substances. This includes chemical-resistant suits, gloves, and masks equipped with respirators.
- Decontamination Equipment: Tools and processes necessary for cleaning individuals and equipment that may have been exposed to hazardous materials.
- Detection Devices: Firefighters learn to use various detection equipment to identify the presence of hazardous materials, including gas detectors and chemical sensors.
By mastering the use of specialized equipment, firefighters increase their safety and effectiveness during emergencies.
c. Emergency Response Protocols
Training encompasses learning emergency response protocols, which include:
- Incident Command System (ICS): Understanding the ICS structure ensures effective communication and coordination during an emergency response involving multiple agencies and personnel.
- Scene Safety Assessment: Assessing the situation to determine risks and identify the best course of action for containment and evacuation of affected individuals.
- Containment Strategies: Learning techniques for containing spills or releases to minimize environmental impact and protect public health.
These protocols are crucial for ensuring the safety of both the responders and the public.
3. Types of Training Programs
There are several organized training programs firefighters can participate in to enhance their skills in handling hazardous materials:
a. Hazardous Materials Awareness Training
Awareness training provides firefighters with a basic understanding of hazardous materials, focusing on:
- Recognition of hazardous materials on the scene, enabling them to initiate response actions safely.
- Understanding Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS): Learning to read and understand safety data sheets that accompany hazardous materials.
b. Hazardous Materials Operations Training
This level of training dives deeper, preparing firefighters for:
- Containment and control measures: Techniques needed to manage small to moderate hazardous materials incidents.
- Incident assessment and decision-making: Practical skills essential for evaluating risks and implementing response plans effectively.
c. Hazardous Materials Technician Training
Technician courses offer advanced skills focusing on:
- Advanced containment and removal techniques: The ability to handle larger incidents involving hazardous materials safely.
- Developing and implementing response plans: Skills to create comprehensive action plans during hazardous material emergencies.
These layered training programs ensure that firefighters can respond competently to hazardous material incidents.
4. Real-World Scenarios and Drills
To reinforce the knowledge gained during theoretical training, firefighters engage in various real-world scenarios and drills. These practices include:
- Simulated Hazardous Material Incidents: Controlled environments allow firefighters to practice their skills in response to mock hazardous materials incidents, ensuring they can apply their training under pressure.
- Coordination with Other Agencies: Training often includes collaboration with local and federal agencies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and hazardous materials response teams, to prepare for multi-agency incidents.
- Post-Incident Analysis: After active drills, firefighters review their actions and decision-making processes to identify strengths and areas for improvement, fostering continuous learning and growth.
These practical exercises ensure firefighters are equipped to handle real-life scenarios effectively and efficiently.
5. The Impact of Advanced Technology on Training
Advancements in technology have significantly influenced how firefighters are trained to handle hazardous materials:
- Virtual Reality (VR) Simulations: VR training provides immersive experiences for firefighters, allowing them to practice hazardous materials protocols in a safe environment.
- Real-Time Data Sharing: Technology allows different agencies to share real-time data on hazardous materials incidents, enhancing decision-making and coordination.
- Drone Technology: Drones can assess hazardous areas remotely, providing critical information before responders enter potentially dangerous situations.
Integrating these advanced technologies into training enhances the safety and preparedness of firefighters.
Conclusion
Training firefighters to handle hazardous materials and dangerous chemicals is not just about extinguishing fires; it’s about protecting lives, property, and the environment. The comprehensive training programs focus on understanding materials, specialized equipment, emergency response procedures, and real-world drilling. As hazardous materials continue to pose a threat in various settings, the importance of well-trained firefighters cannot be overstated. With their expertise, communities can rest assured that brave responders are prepared to face any challenge that arises.
Firefighters embody dedication and courage, continuously enhancing their skills to ensure they can manage hazardous materials incidents, ultimately working towards a safer environment for all.